No workflow is immune from unexpected disruptions. Certainly, errors and issues are bound to occur in operations that involve cross-functional teams and multiple stakeholders. However, what differentiates you in this competitive marketplace is how fast you respond to any quality issue or operational failure.
Evidently, contemporary leadership is more focused on implementing digital technologies to enhance their incident management process. A quality incident not only disrupts routine operations, but also degrades the quality of product or services, causes serious financial implications, and damages your brand’s reputation, which could take years to rebuild. However, more than just being a reactive approach, a well-planned and structured incident management process can save businesses from costly downtimes, legal and compliance risks, and, most importantly, reputational damage.
Let us understand the incident management process in detail and find out ways to optimize it for better outcomes.
What Is the Incident Management Process?
The incident management process reflects a systematic approach designed to effectively detect, record, and resolve quality issues arising from accidents, emergencies, equipment failures, natural disasters, or more. While the primary objective of the incident management process is to restore operations and minimize their impact, it also considers implementing a long-term solution to prevent issues from recurrence.
A well-planned incident management process includes the following key stages: incident identification, reporting, prioritization, diagnosis and resolution, incident closure, and post-closure audits. For industries operating in the regulatory domains, it is mandatory to ensure that the process is compliant with the existing company policies and industry-specific guidelines issued by the regulatory authorities. However, first, let us understand the significance of implementing a robust incident management process.
Why Is Incident Management Important?
1. Minimize operational disruption
Depending on the severity, any unforeseen event in the quality workflow can temporarily disrupt or halt the operations, causing minor downtime to serious operational crisis. However, a well-structured incident management process aims to timely identify, assess, and resolve incidents, ensuring quick response for faster recovery of the operations.
2. Protect customer’s and stakeholder’s trust
Customer and stakeholder trust is the biggest asset that contributes to recurrent sales, and the way organizations handle incidents affects their trust in the brand. While a streamlined incident management process speeds up the incident resolution, it also pours in transparency by thoroughly documenting the process at every stage.
3. Optimize resource allocation and response
Implementing a systematic approach to handle incidents allows organizations to promptly categorize the issues based on their severity and assign stakeholders from cross-functional teams to effectively mitigate the quality incidents.
4. Enhance risk management framework
Organizations having a proper incident management process find it easier to mitigate quality risks before they escalate into much bigger quality issues. Certainly, root cause analysis, streamlined CAPA management, and tracking incident trends are some of the key aspects of incident management that facilitates risk management.
5. Adherence with compliance and regulations
A well-structured incident management process is planned in accordance with the internal policies and regulatory requirements. There are predefined criteria to classify and prioritize incidents and specific protocols, SOPs, and optimized workflows to deal with them. Furthermore, documenting each stage empowers the quality teams to audit and validate the process and ensure that it is compliant with the industry regulations.
Key Steps in the Incident Management Process
1. Incident Identification and Detection
Identifying and recognizing an incident is the first and foremost step of this incident management process. Incidents in regulated industries can lead to financial, reputational, or operational risks. For instance, an incident can be an exposure of Personal Identifiable Information (PII) in banking, unauthorized access to customer’s data in telecom, or an adverse reaction to any drug in the pharmaceutical industry.
However, following industry-specific frameworks or protocols that offer clear guidelines on identifying and resolving incidents can help your incident management teams quickly assess the situation and raise an alert.
2. Incident Reporting
Effectively reporting and categorizing an incident is crucial as soon as it is identified. Gathering adequate evidence and information related to the incident is necessary to assist quality teams in understanding its nature and severity. Certainly, documenting an incident also plays a crucial role in standardizing your organization’s incident management process.
Digital QMS, while offering a centralized space to document incidents, also allows users to create a detailed activity log to ensure adequate transparency and accountability in the process. However, what information do you need to effectively report an incident? Here is a short summary of the form template that can be used:
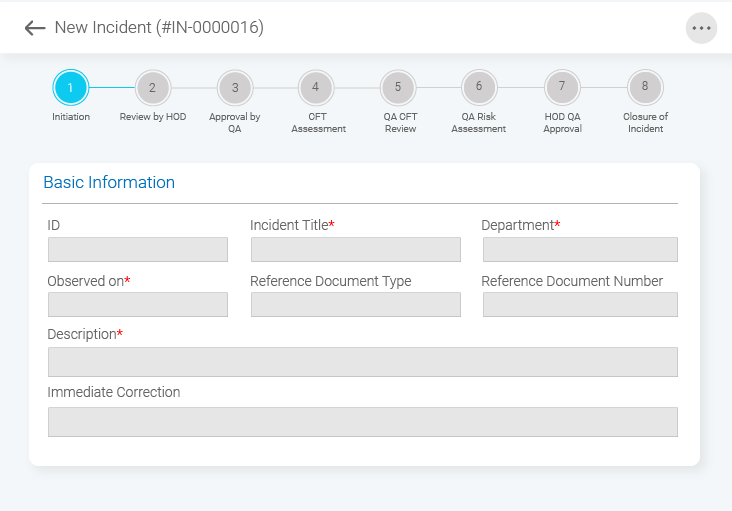
3. Incident Prioritization
Based on the data and facts presented in the supportive documents, the priority of the incident is to be decided to quickly minimize the disruption. Setting up priorities enables organizations to determine the order in which the issues must be addressed and allows them to allocate the available resources adequately.
However, what factors play a deciding role in determining the priority?
- Impact: Up to what extent the incident can disrupt the business operations
- Urgency: Is the incident time sensitive? Will it escalate, causing more damage over time?
- Severity: This maps the potential damage caused by an incident in terms of financial, security, or non-compliance.
- Available resources: Pre-occupancy of personnel or tools can impact the incident management process.
4. Diagnosis and Resolution
Incident prioritization is followed by incident response, which covers two crucial stages: first, identifying the root cause and second, implementing corrective and preventive measures. Let us understand this.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Certainly, repeated incidents can lead to system failure, costly downtime, and loss of business continuity. However, conducting a thorough root cause analysis helps incident response teams to understand the primary cause of the issue. It enables teams to fix the issues from their core and offers a sustainable response, ensuring reliable and stable operational workflow. An in-depth RCA also plays a critical role in outlining clear and effective corrective and preventive actions.
- Temporary Fixes and Permanent Solution Planning and implementing a flawless CAPA process should be the next priority. Certainly, it is a mix of some temporary fixes to minimize the impact of the incident and restore the operations and some permanent solutions to stop preventing similar incidents in the future. The incident management teams prepare a robust action plan to carefully implement and manage effective CAPA, ensuring better quality and compliance in the long term.
5. Incident Closure and Post-Incident Review
After implementing CAPA, tests are performed to verify the effectiveness of the solution, ensuring that the incident no longer affects the operational process. Once the incident has been resolved, it needs formal closure. All the documentation created since the incident was identified to its final resolution is recorded in accessible repositories for future reference. The incident process is audited by internal stakeholders and regulatory bodies to track if it was compliant with the internal policies and regulatory requirements.
The Real-World Use Case of an Incident Management Process
How does the incident management process work in real life? Let us understand the complete process with a real-life use case from a manufacturing industry. Evidently, robotics arms are often used in production lines to automate and speed up manual and repetitive operations like welding, packaging, and material handling. However, a malfunction in the robotic arm may slow down production, increase operational costs, or raise serious quality concerns. Let us see how the incident management team at the manufacturing unit responds to the issue and comes up with a solution.
- The sensors attached to the robotic arm generate an automated alert to raise the malfunction.
- The issue is identified and recorded in a centralized log, along with the supportive evidence.
- The incident is categorized under ‘Machinery Failure’ and the priority is set as ‘Critical.’
- A thorough investigation was conducted. The incident teams studied the maintenance records and equipment specifications and analyzed previous performance data available on the machinery performance dashboard.
- Incident management teams highlighted the failure of the hydraulic pump as the root cause of the incident.
- Reports suggesting the action plan was submitted for approval from the authorized stakeholders.
- Once approved, the hydraulic pump was replaced and tested for efficiency. The operations were restored, and the team created a maintenance schedule and checklist to replace machines that are used to their full capacity.
- Once the operations were fully restored, a thorough incident report was created and sent for approval to formally close the incident.
- All the documentation, including maintenance logs, performance reports, equipment service records, RCA, CAPA plan, etc., were stored for auditing and future reference.
Incident Management Best Practices
1. Standardizing the definition of incidents
Establishing a clear taxonomy and incident classification frameworks becomes essential to standardizing your incident management process. Certainly, having a clear definition of incidents eliminates confusion and helps incident response teams to quickly identify the risk or severity associated with the issues.
2. Timely identification and detection of incidents
Continuous audits of the operations and corrective actions coupled with a thorough analysis of customer feedback and incident trends can help quality teams detect and identify the incidents proactively. Certainly, early detection of issues can prevent them from escalating into more severe problems.
3. Effective communication and documentation
Having a centralized hub to facilitate cross-functional communication, collaboration, and file sharing can amplify the efforts of your incident management teams. It reduces confusion, promotes continuous improvements, and establishes a culture of openness and transparency.
4. Create easy-to-understand templates for standard documents
With digital incident management system, you can create standardized templates to report, track, and analyze incidents. This saves time, considers the necessary details, and ensures that the process is documented in a uniform way for better consistency, clarity, and compliance.
5. Analyze previous data
Carefully assessing past incident records allows quality assurance teams to quickly identify trends and patterns and proactively look for possible incidents that can arise in the near future. This speeds up incident response and contributes to better decision-making.
BizPortals QMS: Outlining a New Way Forward
With rapidly evolving workplace technologies, the traditional and paper-based quality management processes have been replaced by a digital QMS. Certainly, digital QMS have played a crucial role in streamlining and automating the quality processes within the organization.
On the same lines, BizPortals QMS, a SharePoint-based incident management solution, has helped modern businesses to amplify their efforts to stay compliant and deliver quality products and services to their customers.
While offering a centralized platform to track, report, log, and manage incidents, it empowers cross-functional teams to access and share documents and collaborate on them effectively for faster resolutions. Furthermore, robust document control features, such as versioning, role-based access, and multi-level permissions, ensure that the critical information is secure and accessible only to the authorized personnel.
Users can now create standard templates with customizable fields for reports and forms to bring consistency and operational efficiency. It also enables them to implement automated workflows and integrate them with automated email notifications and digital signatures to fasten the approval processes.
Curious about the features of BizPortals QMS? Schedule a free live demo to experience them firsthand.
Get Free Product Tour

